[1] "state,abb,region,population,total" "Alabama,AL,South,4779736,135"
[3] "Alaska,AK,West,710231,19" Data Importing
MATH/COSC 3570 Introduction to Data Science
Dr. Cheng-Han Yu
Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences
Marquette University
Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences
Marquette University









DBI, jsonline, xml2, httr
R Data Importing
Rectangular Data
readr 📦 Functions
| Function | Format | Typical suffix |
|---|---|---|
read_table() |
white space separated values | txt |
read_csv() |
comma separated values | csv |
read_csv2() |
semicolon separated values | csv |
read_tsv() |
tab delimited separated values | tsv |
read_fwf() |
fixed width files | txt |
read_delim() |
general text file format, must define delimiter | txt |
Be careful: The suffix usually tells us what type of file it is, but no guarantee that these always match.
Reading Data
read_csv() prints out a column specification giving us delimiter, name and type of each column.
murders_csv <- read_csv(file = "./data/murders.csv")
# ── Column specification ─────────────
# Delimiter: ","
# chr (3): state, abb, region
# dbl (2): population, total
head(murders_csv)# A tibble: 6 × 5
state abb region population total
<chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Alabama AL South 4779736 135
2 Alaska AK West 710231 19
3 Arizona AZ West 6392017 232
4 Arkansas AR South 2915918 93
5 California CA West 37253956 1257
6 Colorado CO West 5029196 65Missing Values
Which type is the column vector x? Why?
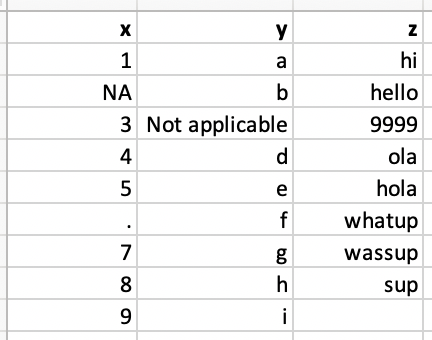
Solution 1: Explicit NAs
- By default,
read_csv()only recognizes ” “ and NA as a missing value. - Specify the values that are used to represent missing values by argument
na.
Solution 2: Specify Column Types
Column Types
| type function | data type |
|---|---|
col_character() |
character |
col_date() |
date |
col_datetime() |
POSIXct (date-time) |
col_double() |
double (numeric) |
col_factor() |
factor |
col_guess() |
let readr guess (default) |
col_integer() |
integer |
col_logical() |
logical |
col_number() |
numbers mixed with non-number characters |
col_numeric() |
double or integer |
col_skip() |
do not read |
col_time() |
time |
Writing Data
# A tibble: 3 × 2
x y
<dbl> <chr>
1 1 a
2 2 b
3 3 c
read_rds() and write_rds()
- We save an R object (usually a data set) in
.Rdsin the R binary file format. 1
10-Import Data
- If you haven’t, install and load the
tidyversepackage.
In lab.qmd ## Lab 10 section,
- Import ssa_male_prob.csv and ssa_female_prob.Rds in the data folder using
read_csv()and call themssa_maleandssa_female, respectively.
- Plot
Age(x-axis) vs.LifeExp(y-axis) forFemale. The type should be “line”, and the line color is red. Add x-label, y-label and title to your plot.
- Use
lines()to add a line ofAge(x-axis) vs.LifeExp(y-axis) forMaleto the plot. The color is blue.
Read Excel Data
readxl 📦 Functions
| Function | Format | Typical suffix |
|---|---|---|
read_excel() |
auto detect the format | xls, xlsx |
read_xls() |
original format | xls |
read_xlsx() |
new format | xlsx |
- The Microsoft Excel can have more than one sheet in one file.
- The functions above read the first sheet by default.
- The
excel_sheets()gives us the names of all the sheets in an Excel file.
Sheet Names
- The sheet names can be passed to the
sheetargument to read sheets other than the first.
[1] "Sheet1" "Sheet2" "Sheet3"# A tibble: 19 × 6
Scores `131024` `113804` `104201` `103886` `91756`
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 10 NA 64 8 227 34
2 11 6 83 11 217 58
3 12 23 87 7 28 67
4 13 1 54 16 230 42
5 14 3 145 18 303 57
6 15 58 151 50 192 98
7 16 1 129 13 156 125
8 17 73 214 59 163 115
# ℹ 11 more rows
pd.read_csv
pd.read_excel
pd.DataFrame.to_csv
pd.read_csv
pd.DataFrame.to_csv
w = {"x":[1, 2, 3],
"y":['a', 'b','c']}
wdf = pd.DataFrame(w)
wdf.to_csv("./data/wdf.csv")
mydf = pd.read_csv('./data/wdf.csv')
mydf.head() Unnamed: 0 x y
0 0 1 a
1 1 2 b
2 2 3 c